A conducting bar mass m and length l moves on two frictionless parallel conducting rails in the presence of a uniform magnetic field B_0 directed int. The voltage source maintains a constant current I in the rails and bar and a constant uniform vertical magnetic field.
A Conducting Bar Of Mass M And Length L Moves On Two Frictionless Parallel Rails In The Presence Of A Constant Uniform Magnetic Field Of Magnitude Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online
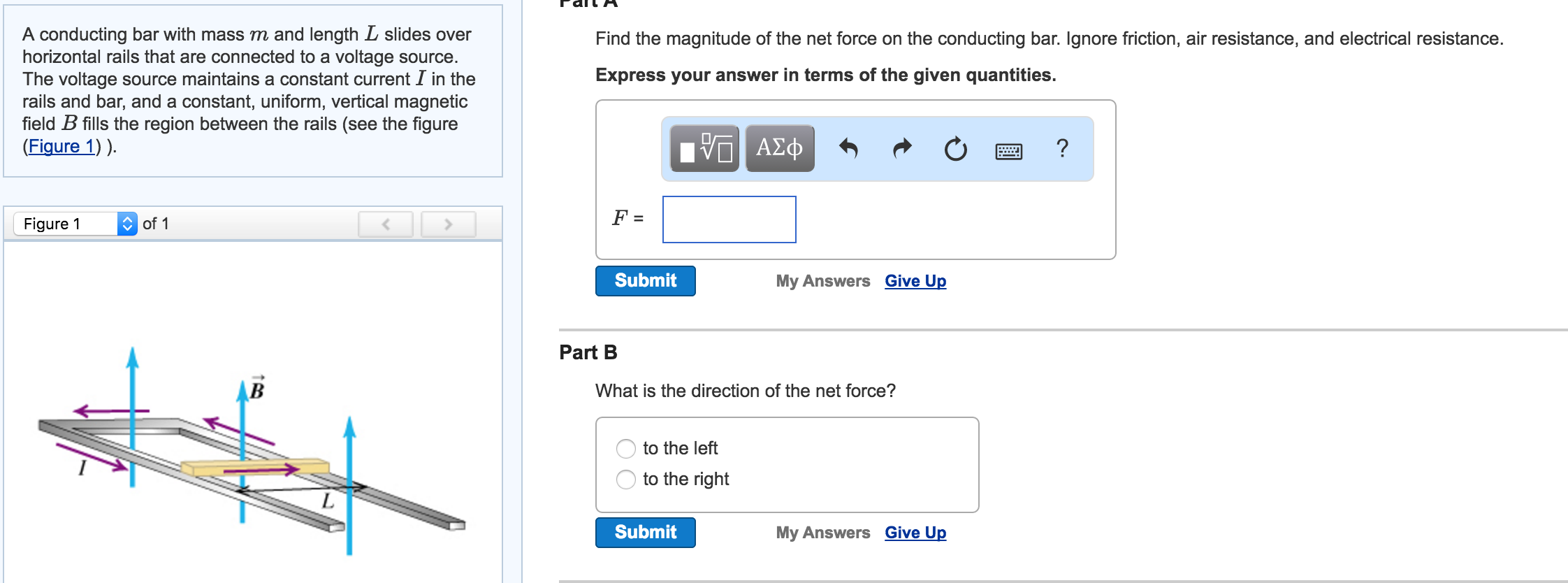
A conducting bar with mass m and length L slides over horizontal rails that are connected to a voltage source.

. The bar is released from rest and slides down the rails. An Electromagnetic Rail Gun A conducting bar with mass m and length L slides over horizontal rails that are connected to a voltage source. The rails have negligible resistance.
A conducting bar with mass m and length L slides over horizontal rails that are connected to a voltage source. The ring and the bar are connected by a resistor R 10. A conducting bar with mass m and length L slides over horizontal rails that are connected to a voltage source The voltage source maintains a constant current I in the rails and bar and a constant uniform vertical magnetic field B fills the region between the rails see the figure Figure 1 Find the magnitude of the net force on the conducting bar.
The voltage source maintains a constant current I in the rails and bar and a constant uniform vertical magnetic field B fills the region between the rails Fig. Find an expression for the. A conducting bar with mass m and length L slides over horizontal rails that are connected to a voltage source.
A current I is fed into the bar at the pivot so that it flows from center to edge of the circle. A conducting bar of mass m and length l moves on two frictionless parallel rails in the presence of a constant uniform magnetic field of magnitude B directed into the page as shown in the figure. The voltage source maintains a constant current I in the rails and bar and a constant uniform vertical magnetic field B fills the region between the rails see the figure Figure 1.
In which direction into or out of the page will a current through the conducting bar cause the bar to experience a force to the right. Find the magnitude and direction of the net force on the conducting bar. Question From Cengage BM Sharma MAGNETISM AND ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION MAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES JEE.
In which direction into or out of the page will a current through the conducting bar cause the bar to experience a force to the right. A metal bar with length L mass m and resistance R is placed on frictionless metal rails that are inclined at an angle above the horizontal. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude is directed downward in the figure B.
A conducting bar of length l and mass m rests at the left end of the two frictionless rails of length d in the figure. The voltage source maintains a constant current I in the rails and bar and a constant uniform vertical magnetic field B fills the region between the rails see the figure Figure 1 Figure 1 of 1 Aramak icin Part A Find the magnitude of the. A conducting bar of mass m and length l moves on two frictionless parallel rails in the presence of a constant uniform magnetic field of magnitude B directed into the page as shown in the figure.
A uniform magnetic field of strength B points upward. A conducting bar with mass m and length L slides over horizontal rails that are connected to a voltage source. You know that acceleration is given.
A uniform magnetic field B to the rotating plane of the bar and the ring. A uniform conducting bar of mass m and length L is pivoted at one end. A conducting bar with mass m and length L slides over horizontal rails that are connected to a voltage source.
The ring and the bar are connectedby a resistor R 10. A conducting bar of length l and mass m rests at the left end of the two frictionless rails of length d in FIGURE P2975. A and M on By Do Newtons Law.
A conducting bar of mass m and length l moves on two frictionless parallel rails in the presence of a constant uniform magnetic field of magnitude B direct. The bar rotates about the pivotpoint o which is also the center of the ring. A uniform magnetic field of strength B points upward.
A conducting bar of mass m 1kg and length l 1m is in contact with a thinconducting circular ring as shown in the figure. The bar rotates about the pivot 3D point o which is also the center of the ring. The bar is given an initial velocity v 0 towards the right at t 0.
The voltage source maintains a constant current I in the rails and bar and a constant uniform vertical magnetic field B fills the region. We know that the force accepted by the magnetic field its given by i times L A. Times Steve signed five fives The Angle between L.
The bar is given an initial velocity v 0 towards the right at t 0. At the other end it makes electrical contact through brushes with a conductor shaped like a ring of radius L so that the bar forms a radius of the circle. The bar is given an initial velocity v0 towards the right at t 0.
The voltage source maintains a constant current I in the rails and bar and a constant uniform vertical magnetic field B fills the region between the rails. Part A Find the magnitude of the net force on the conducting. A conducting bar of mass m 1kg and length l 1m is in contact with a thin conducting circular ring as shown in the figure.
. A conducting bar of mass m and length l moves on two frictionless parallel rails in the presence of a constant uniform magnetic field of magnitude B directed into the page as shown in the figure.

A Conducting Bar Of Length L Moves To The Right On Two Frictionless Rails As Shown Youtube

A Conducting Bar Of Mass M And Length L Moves On Two Frictionless Parallel Rails In The Presence Of A Constant Uniform Magnetic Field Of Magnitude B Directed Into The Page As
Solved A Conducting Bar With Mass M And Length L Slides Over Chegg Com
0 Comments